D5. Activating Objects in VR

Learning Outcomes
- Explain how activation events work in Unity’s XR and UI systems. Before class, review how components like
XRBaseInteractableandButtonexpose UnityEvents such asOnSelectEntered()andOnClick()to trigger animations, sounds, or state changes.- Apply event-driven design principles in Unity XR projects. In preparation, explore the roles of events, listeners, and handlers, and set up UnityEvents to call specific methods—for example, triggering robot animations in a state-based system.
- Implement feedback mechanisms to enhance user interactions. Ahead of the session, experiment with visual, audio, and haptic cues to make system responses clear, using tools like the
RobotFeedbackManagerto play sounds or highlight objects.- Design contextual interactions based on system state. Come prepared by creating or testing conditional flows where activation inputs are gated by readiness states, and add clear visual and audio alerts when interactions are blocked.
Activation Events
Activation events in VR refer to specific triggers or signals that are generated when a user interacts with a virtual object or environment in a meaningful way. These events typically indicate a change in state or the initiation of an action based on user input. An activation event might occur when a user presses a button on a VR controller while grasping a virtual object, causing the object to perform an action such as opening, lighting up, transforming, or being thrown. They are used to provide feedback (e.g., trigger sounds, change indicator lights, or update display panels), initiate processes (e.g., start machinery, toggle system states, or signal a change in a simulation), and decouple actions (e.g., separate the user input from the actions performed, enabling modular programming). Key principles include:
-
Event-Driven Design: Activation events follow an event-driven design. When an event is detected (such as a button press), one or more functions execute. This modularity simplifies management and adapts well to complex engineering workflows.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Effective VR systems use both auditory (sounds) and visual (lighting, material changes) feedback. These cues are vital in engineering environments for communicating machine states and ensuring operator awareness.
-
Contextual Interactions: Activation events should reflect the current system state, enabling or restricting interactions based on context (e.g., safety conditions, system readiness). This ensures realistic and safe behavior, mirroring industrial safety protocols.
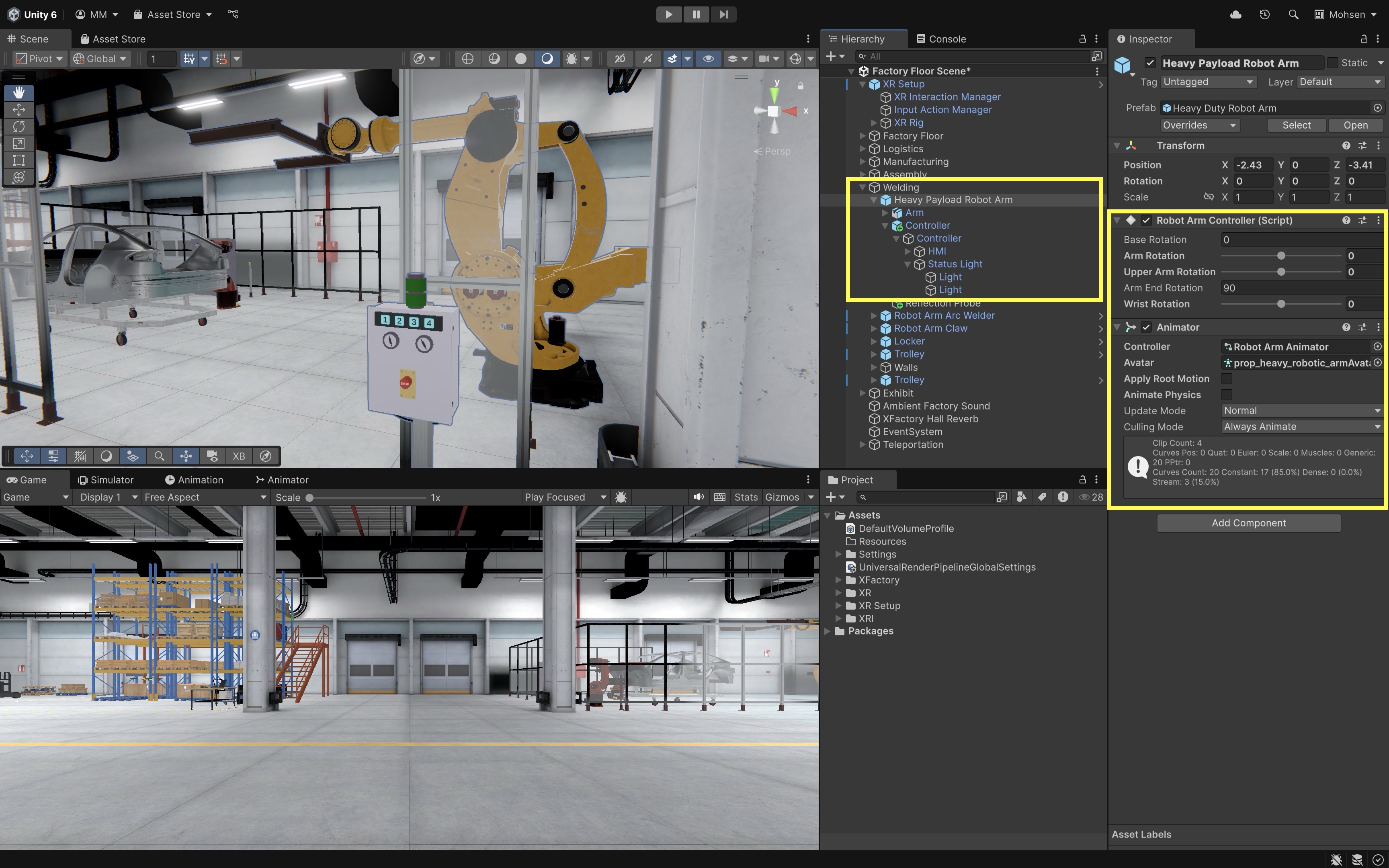
In the welding station of XFactory, pressing a virtual button on the
Controllerbox with a touch-enabled numpad can trigger activation events for theHeavy Payload Robot Arm. For instance, pressing1could activate thePickanimation by setting the corresponding trigger in theAnimator Controller(event-driven design). Upon activation, the system plays a confirmation beep, theStatus Lightindicator on theControllerbox changes from green to red, and theHeavy Payload Robot ArmGameObject begins moving to pick up the car body from the trolly (feedback mechanism). If the emergency stop button at the welding station is engaged, pressing any number on the numpad will not activate the robot. Instead, a red flashing light is shown and an error buzzer sounds, indicating that activation is disabled until the emergency stop is cleared (contextual interaction).
Event-Driven Design
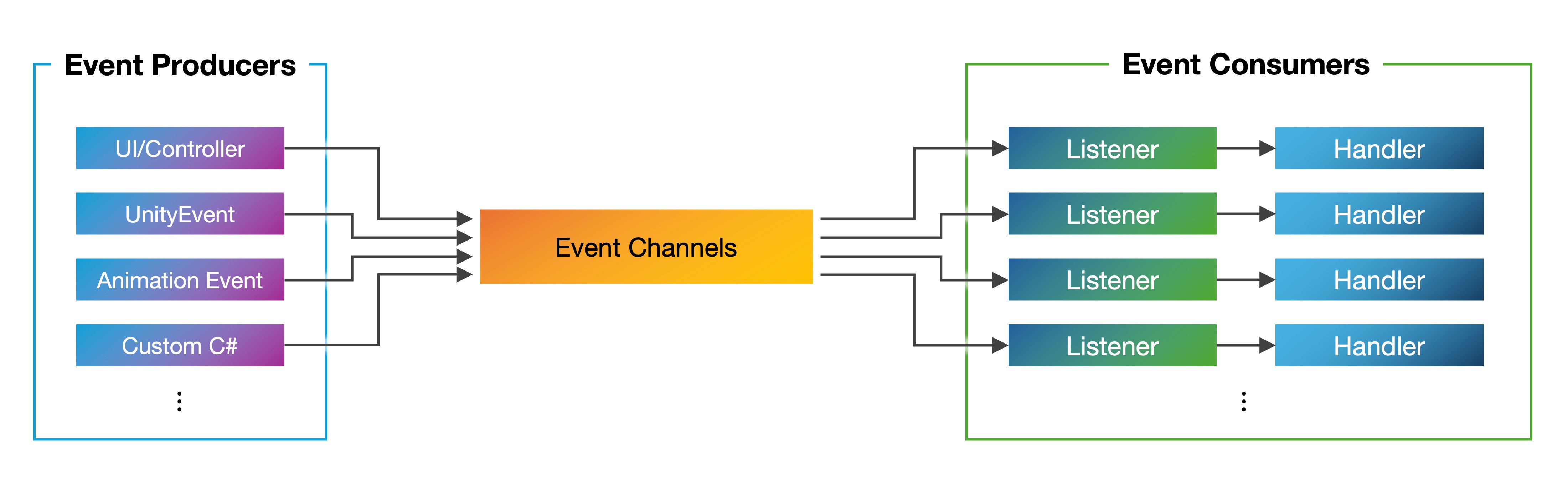
Event-driven design is a software architecture pattern where the flow of control is governed by the occurrence and handling of events rather than a fixed, linear execution path. In immersive VR applications—where user interactions, physics simulations, environmental changes, and external data streams happen simultaneously and often unpredictably—this model is especially effective. It enables real-time responsiveness, modular growth, and maintainable interaction logic. Key concepts to understand:
-
Event: A discrete signal that something has happened. In VR, this might be a user squeezing a controller trigger, a collision between two virtual objects, or the player entering a certain zone. Events often include extra data—like a position vector, a timestamp, or a user ID—that helps the system decide what to do next.
-
Listener (Subscriber): A piece of code that says, “I care about this type of event.” Listeners register with the event system at startup or during gameplay. When the matching event occurs, the system calls the listener’s handler. This way, components don’t need to constantly check for changes—they just wait until something happens.
-
Event Handler: The function that runs when an event occurs. Handlers should be kept lightweight to avoid slowing down the VR experience—for example, they might just update state or trigger an animation, while leaving heavier work to specialized systems.
-
Modularity: By defining a clear set of event types, you can create independent modules (input devices, physics engines, UI panels) that only communicate through events. This makes it simple to swap parts—for example, upgrading from a controller to hand-tracking—without breaking the rest of the app.
-
Decoupling: In an event-driven system, no module needs a direct reference to another. Any part of the code can emit an event, and any other part can listen for it. This reduces interdependencies, makes unit testing easier (you can fire fake events), and prevents small changes from rippling through the entire codebase.
UI-based Activation
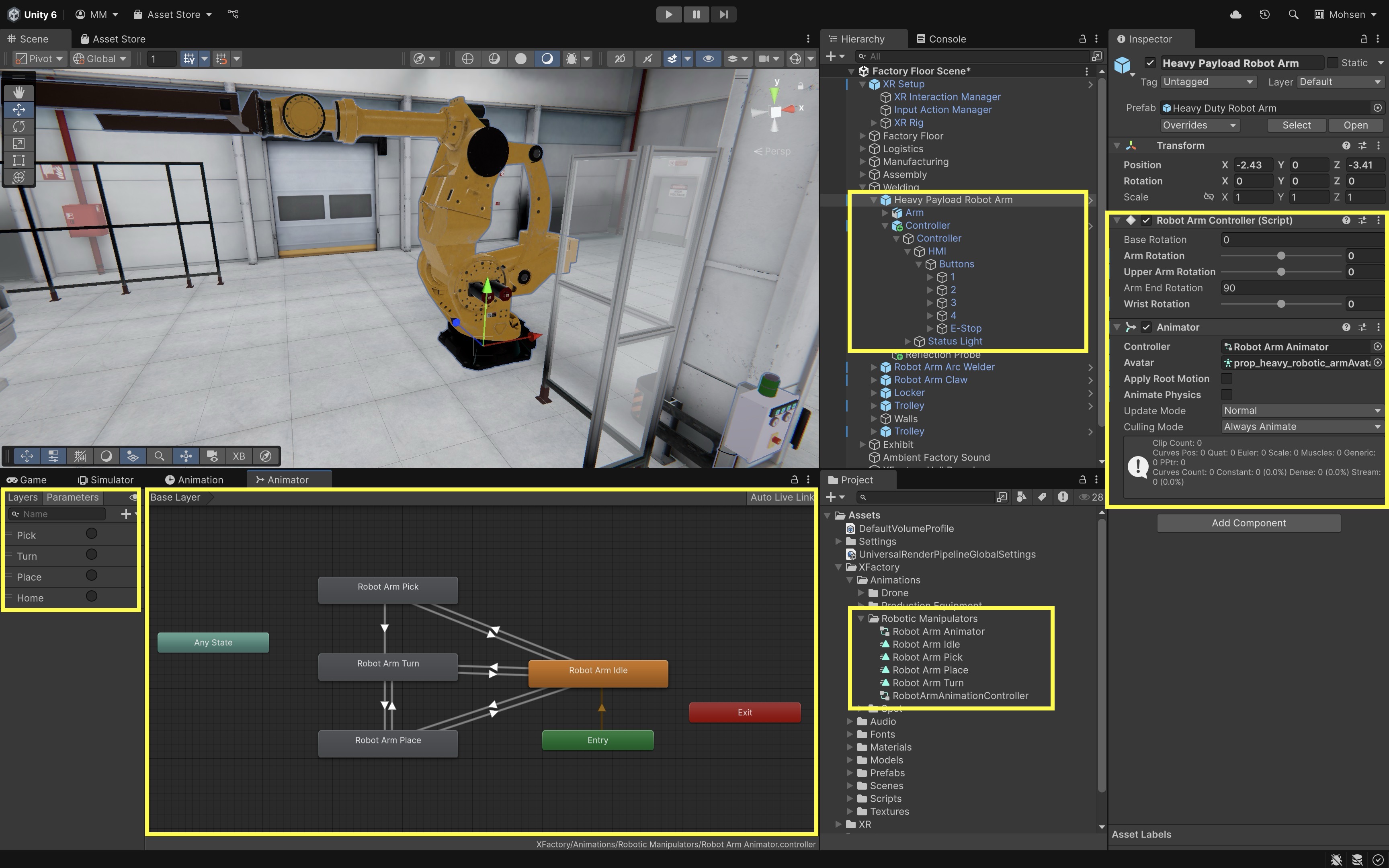
At the welding station of XFactory, the user controls a heavy-duty robot arm using a numpad with four configurable buttons. Each button maps to a different action (e.g., Pick, Turn, Place, Home). These actions trigger the corresponding animation state and update the system’s status indicator. Our goal is therefore to (1) map each numpad button (1–4 GameObjects) to an animation trigger (Pick, Turn, Place, Home) on the robot arm’s Animator, (2) log each activation to the console, and (3) change the status light color based on whether the robot is idle or moving.
- Setup the Animator Triggers:
- Go to the robot arm’s
Animator Controller. - Add or verify states:
Idle,Pick,Turn,Place. - Add or verify transitions using
Trigger Parameters:"Home","Pick","Turn","Place".
- Go to the robot arm’s
- Create the
RobotControllerScript:- Prepare a
RobotController.csscript to manage the robot arm’s animation triggers and updates a status light to reflect whether the robot is active (moving) or idle. A script can help synchronize visual feedback with animation states in a modular, event-driven way.
using UnityEngine; public class RobotController : MonoBehaviour { public Animator robotAnimator; public GameObject statusLight; public Material greenMaterial; public Material redMaterial; private Renderer statusRenderer; // Name of the idle state as it appears in the Animator private const string idleStateName = "Robot Arm Idle"; private void Start() { if (statusLight != null) statusRenderer = statusLight.GetComponent<Renderer>(); } private void Update() { if (robotAnimator == null || statusRenderer == null) return; bool isInTransition = robotAnimator.IsInTransition(0); AnimatorStateInfo currentState = robotAnimator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0); // Light should only be green if not in transition and fully in the idle state bool isTrulyIdle = !isInTransition && currentState.IsName(idleStateName); statusRenderer.material = isTrulyIdle ? greenMaterial : redMaterial; } public void TriggerAnimation(string triggerName) { if (robotAnimator == null) return; robotAnimator.SetTrigger(triggerName); Debug.Log($"Robot Triggered: {triggerName}"); // Status light will update automatically in Update() } } - Prepare a
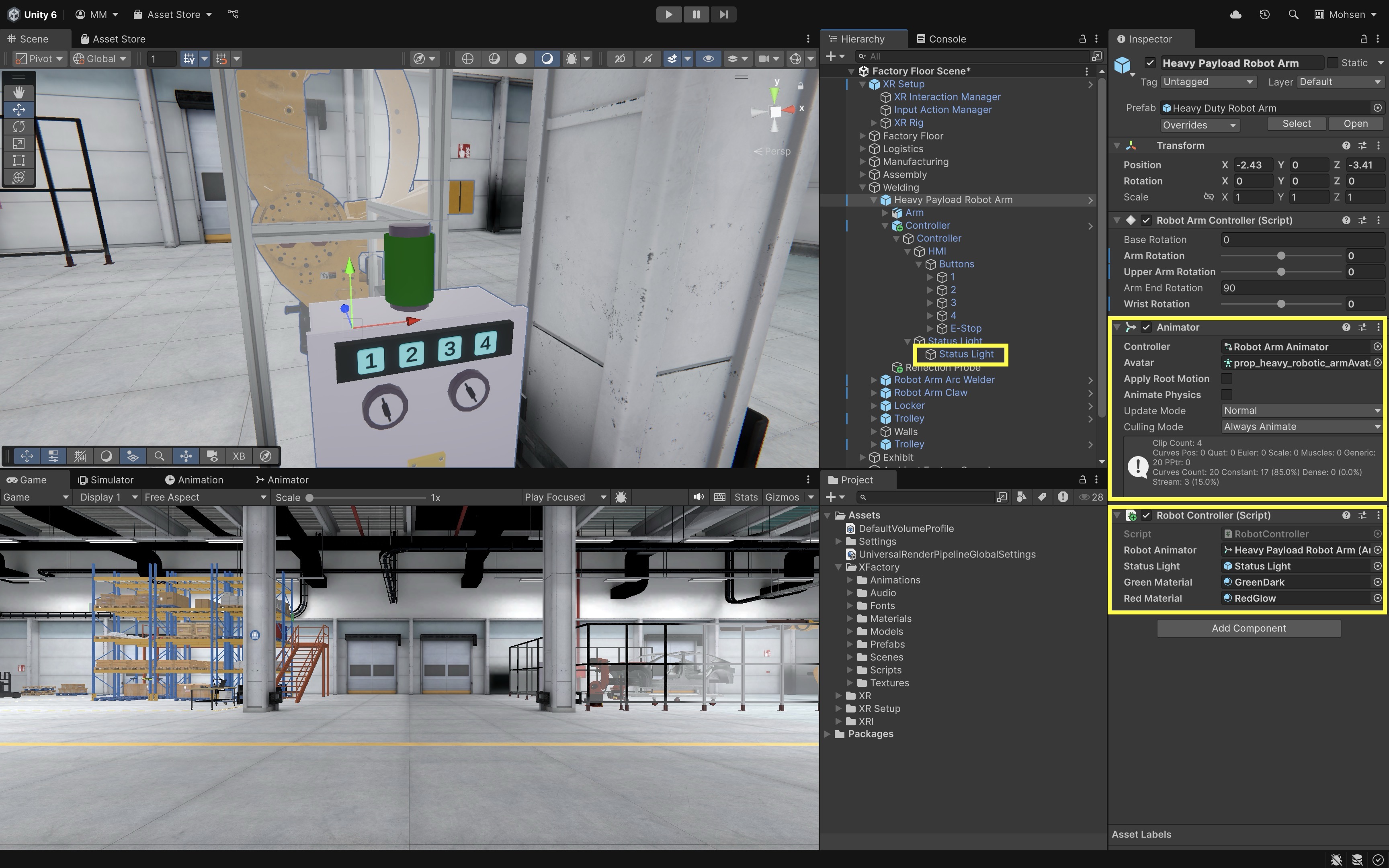
- Configure the Script:
- Attach the script to a GameObject representing the robot (e.g.,
Heavy Payload Robot Arm). Robot Animator: Assign theAnimatorcomponent that controls the robot’s state machine.Status Light: AssignStatus Light.Green Material: Assign a status material to show the robot is idle.Red Material: Assign a status material used when the robot is moving.
- Attach the script to a GameObject representing the robot (e.g.,
- Configure the Numpad Buttons:
- From each numpad button, locate the
OnClick()event, - Click the
+to add a new event. - Drag the robot GameObject (with the
RobotController.csscript) into the field. - Select
RobotController → TriggerAnimation(string). - Enter the corresponding animation trigger in the string field (e.g.,
Home,Pick,Turn, orPlace). - Repeat this process for each numpad button, assigning the desired trigger to each.
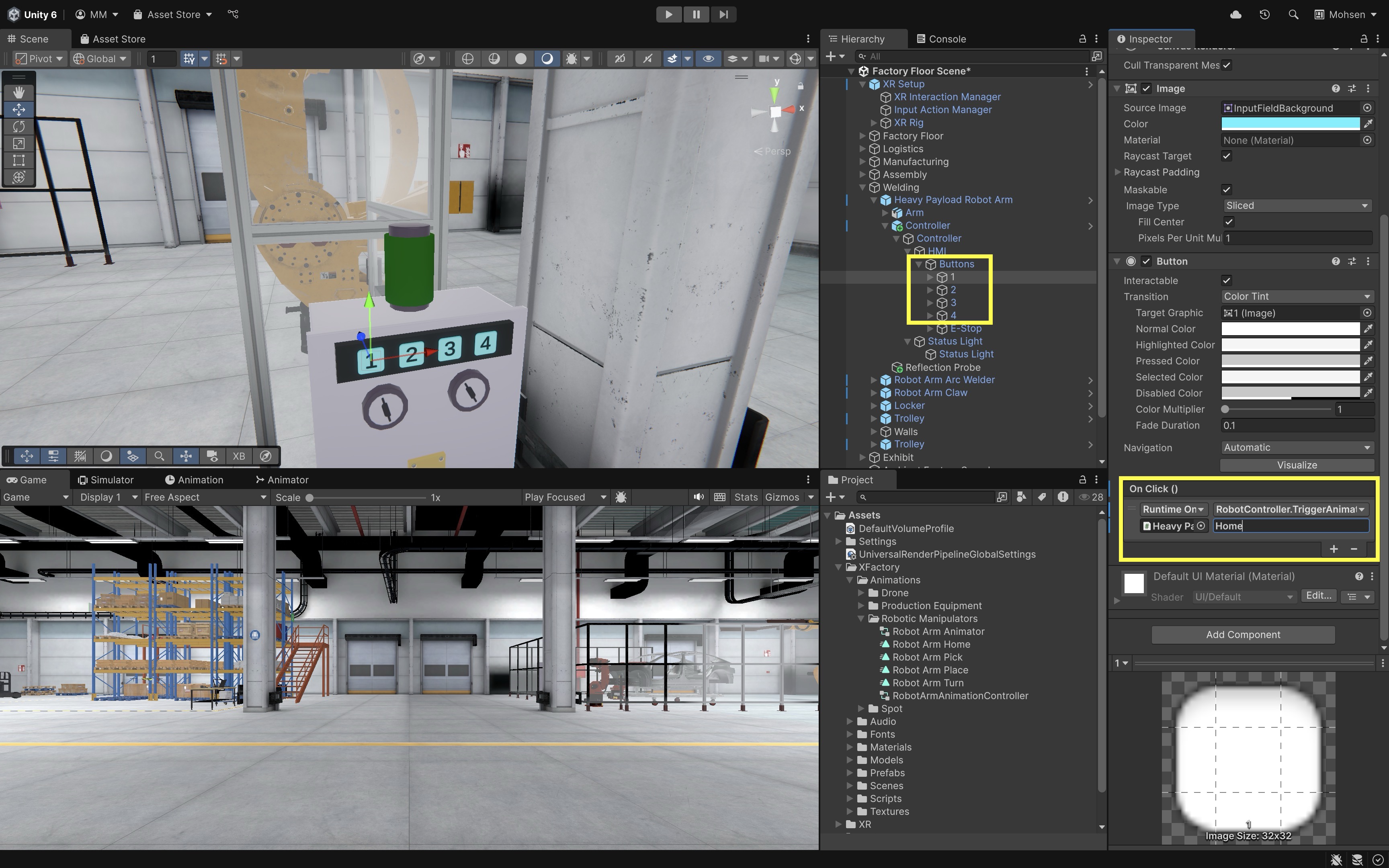
- From each numpad button, locate the
- (Optional) Use a Configurable Button Mapping:
- To make the system flexible, create a script that allows users to assign animation triggers to each numpad button using a dictionary.
- Update your
RobotControllerscript as follows:
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections.Generic; public class RobotController : MonoBehaviour { public Animator robotAnimator; public GameObject statusLight; public Material greenMaterial; public Material redMaterial; private Renderer statusRenderer; // Name of the idle state as it appears in the Animator private const string idleStateName = "Robot Arm Idle"; // Configurable mapping from button numbers to animation triggers public Dictionary<int, string> buttonMappings = new Dictionary<int, string>() { { 1, "Pick" }, { 2, "Turn" }, { 3, "Place" }, { 4, "Home" } }; private void Start() { if (statusLight != null) statusRenderer = statusLight.GetComponent<Renderer>(); } private void Update() { if (robotAnimator == null || statusRenderer == null) return; bool isInTransition = robotAnimator.IsInTransition(0); AnimatorStateInfo currentState = robotAnimator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0); bool isTrulyIdle = !isInTransition && currentState.IsName(idleStateName); statusRenderer.material = isTrulyIdle ? greenMaterial : redMaterial; } // This method is called from UI or XR button events public void OnButtonPressed(int buttonId) { if (buttonMappings.ContainsKey(buttonId)) { TriggerAnimation(buttonMappings[buttonId]); } else { Debug.LogWarning($"Button ID {buttonId} not mapped to any trigger."); } } public void TriggerAnimation(string triggerName) { if (robotAnimator == null) return; robotAnimator.SetTrigger(triggerName); Debug.Log($"Robot Triggered: {triggerName}"); // Status light updates automatically in Update() } } - Configure the Script:
- Select the button GameObject in the
Hierarchy(e.g.,1,2, …). - In the
OnClick()event section, click the+button and drag the robot GameObject (which has theRobotController.csscript attached) into the event field. - From the function dropdown, select
RobotController → OnButtonPressed(int). - Enter the appropriate button number into the parameter field: Button 1 →
1, Button 2 →2, etc. - This will call the correct animation trigger for each button based on the dictionary mapping.
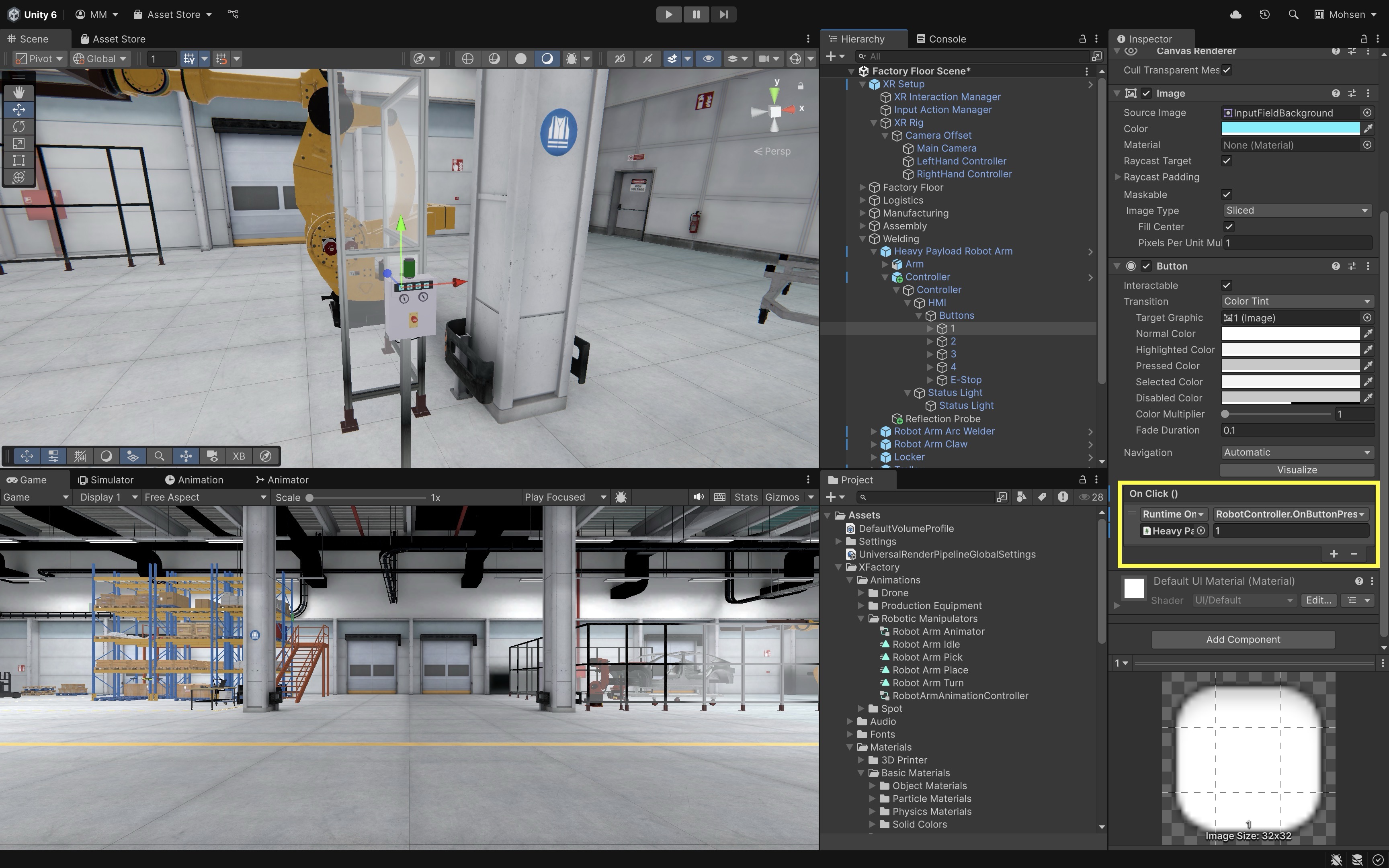
This setup allows you to change button-to-trigger mappings in one place (in the
buttonMappingsdictionary) and easily support reconfiguration via menus or UI tools. - Select the button GameObject in the
- Deploy and Test:
- Deploy the app to your device.
- Each button press on the XR numpad sends a configurable command to the robot.
- The robot’s animation state changes via an
Animatortrigger. - A red or green status light reflects active vs. idle states.
- Console logging supports debugging or monitoring.
- All interactions are modular, extensible, and VR-ready.
Controller & Proximity Activation
In C4. UnityEngine Namespaces, we controlled the door and scene loading using keyboard inputs. Now, let’s update the script to use event-driven activation in VR: the door only responds when the player is within 2 meters and presses the X button on the left controller. This demonstrates how combining proximity events with controller input can create more natural, immersive interactions in virtual environments. Instead of relying on fixed keys, the system now reacts to the player’s presence and actions in 3D space, highlighting the power of event-driven design in VR applications. Replace the previous script with the following:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.SceneManagement;
using UnityEngine.XR; // XR input
public class FactoryYardLoader : MonoBehaviour
{
[Header("Scene")]
public string exteriorSceneName = "Factory Yard Scene";
[Header("Door Settings")]
public float rotationSpeed = 60f; // how fast door rotates
public float openAngle = 120f; // how far door swings open
[Header("Interaction")]
public Transform player; // player or XR rig
public float interactDistance = 2f; // trigger distance
private Quaternion closedRotation; // initial door rotation
private Quaternion openRotation; // target open rotation
private bool opening = false;
private bool closing = false;
private bool sceneLoaded = false;
// XR input
private InputDevice leftHand; // left controller
private bool prevPrimaryButton = false; // button state last frame
void Start()
{
closedRotation = transform.rotation;
openRotation = closedRotation * Quaternion.Euler(0f, -openAngle, 0f);
InitializeLeftHand(); // get left controller
}
void InitializeLeftHand()
{
leftHand = InputDevices.GetDeviceAtXRNode(XRNode.LeftHand);
}
void Update()
{
if (!leftHand.isValid) InitializeLeftHand();
// check if player is close enough
bool inRange = player != null &&
Vector3.Distance(player.position, transform.position) <= interactDistance;
// read primary button (A/X depending on device)
bool primaryButton = false;
if (leftHand.isValid)
leftHand.TryGetFeatureValue(CommonUsages.primaryButton, out primaryButton);
// true only when button pressed this frame
bool primaryPressedThisFrame = primaryButton && !prevPrimaryButton;
// decide open or close
if (inRange && primaryPressedThisFrame && !opening && !closing)
{
float toOpen = Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, openRotation);
float toClosed = Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, closedRotation);
if (toOpen > toClosed) opening = true;
else closing = true;
}
// opening motion + scene load
if (opening)
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(
transform.rotation, openRotation, rotationSpeed * Time.deltaTime);
if (!sceneLoaded &&
Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, closedRotation) > openAngle * 0.25f)
{
SceneManager.LoadScene(exteriorSceneName, LoadSceneMode.Additive);
sceneLoaded = true;
Debug.Log("Factory Yard Scene loaded.");
}
if (Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, openRotation) < 0.1f)
opening = false;
}
// closing motion + scene unload
if (closing)
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.RotateTowards(
transform.rotation, closedRotation, rotationSpeed * Time.deltaTime);
if (Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, closedRotation) < 0.1f)
{
closing = false;
if (sceneLoaded && SceneManager.GetSceneByName(exteriorSceneName).isLoaded)
{
SceneManager.UnloadSceneAsync(exteriorSceneName);
sceneLoaded = false;
Debug.Log("Factory Yard Scene unloaded.");
}
}
}
prevPrimaryButton = primaryButton; // store for next frame
}
}
In the Inspector, assign Player Setup to the Player field. Deploy and test.
Feedback Mechanisms
In interactive VR systems—particularly in engineering and industrial contexts—feedback mechanisms deliver critical sensory cues that inform users about system status, guide their actions, and help prevent errors. By mimicking or augmenting real-world signals, these mechanisms boost immersion, build operator confidence, and reduce safety risks. In VR engineering scenarios, feedback should emulate industrial realities: machines emit characteristic sounds when they engage, warning indicators flash during overload conditions, and tools vibrate to signal contact or completion—ensuring users react as they would on a real factory floor.
Core Concepts
-
Visual Feedback: Changes in lighting, color, UI elements, or animations that signal state transitions or alerts. For example, a virtual valve might glow green when open and pulse red when overheating; status panels can fade in when a sensor reading crosses a threshold. Visual feedback leverages our spatial vision to highlight important information without breaking immersion.
-
Auditory Feedback: Sound cues—such as motor whirrs, warning beeps, confirmation chimes, or verbal prompts—used to reinforce or substitute visual signals. In a VR factory simulation, machinery startup might be accompanied by a deep hum, and an approaching forklift could emit a horn blast. Audio feedback ensures operators notice out-of-view events and can maintain focus on critical tasks even when their gaze is occupied.
-
Tactile (Haptic) Feedback: Vibration patterns or force feedback delivered through controllers, gloves, or exoskeletons to simulate touch, resistance, or impacts. For instance, you might feel a sharp pulse when a robotic arm grips a component or a sustained rumble when drilling. Haptics convey weight, texture, and collision in VR, reinforcing hand–eye coordination and improving manipulation accuracy.
-
Multimodal Feedback: The coordinated use of visual, auditory, and tactile signals to create redundant and complementary cues. A high-pressure valve might flash a warning light (visual), emit a rising alarm tone (auditory), and trigger a vibration warning in the controller (haptic) simultaneously. By engaging multiple senses, multi-modal feedback minimizes the chance of missed signals and supports faster, more intuitive responses in complex, safety-critical operations.
Audio & Haptic Feedback
At the welding station of XFactory, the heavy payload robot arm gives the user real-time multi-modal feedback when a robot action is triggered. It includes (1) audio feedback, playing sounds for movement and idle, (2) visual feedback, flashing the button that was last pressed, and (3) haptic feedback, sending a short vibration to the VR controller when the robot begins to move. Here is how to implement it:
- Create a Script:
- Add a
RobotFeedbackManager.csscript to a central object in your scene (e.g., an emptyRobotFeedbackManagerGameObjet), or to the robot itself (Heavy Payload Robot Arm). - Copy the following script into your IDE.
using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.UI; using System.Collections; using UnityEngine.XR.Interaction.Toolkit.Inputs.Haptics; public class RobotFeedbackManager : MonoBehaviour { [Header("Audio Feedback")] public AudioSource audioSource; // plays robot sounds public AudioClip motorHumClip; // sound when moving public AudioClip idleBeepClip; // sound when idle [Header("Visual Button Feedback")] public float flashDuration = 0.5f; // total flash time public Color flashColor = Color.yellow; // flash color public float flashInterval = 0.1f; // on/off speed [Header("Haptic Feedback")] [Tooltip("HapticImpulsePlayer on hand/controller")] public HapticImpulsePlayer hapticPlayer; // XR vibration [Range(0f, 1f)] public float hapticAmplitude = 0.7f; public float hapticDuration = 0.2f; public float hapticFrequency = 0f; // optional frequency private Coroutine flashRoutine; // reference to flashing public void OnRobotStartMoving() { PlaySound(motorHumClip); // play hum + vibrate SendHaptics(); } public void OnRobotReturnToIdle() { PlaySound(idleBeepClip); // play idle beep } public void FlashButton(GameObject button) { if (button == null) return; var img = button.GetComponent<Image>(); // 2D UI button if (img != null) { if (flashRoutine != null) StopCoroutine(flashRoutine); flashRoutine = StartCoroutine( FlashUIRoutine(img) ); return; } var rend = button.GetComponent<Renderer>(); // 3D object if (rend != null) { if (flashRoutine != null) StopCoroutine(flashRoutine); flashRoutine = StartCoroutine( Flash3DRoutine(rend) ); } } private IEnumerator FlashUIRoutine(Image img) { Color originalColor = img.color; float elapsed = 0f; while (elapsed < flashDuration) { img.color = flashColor; yield return new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); elapsed += flashInterval; img.color = originalColor; yield return new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); elapsed += flashInterval; } img.color = originalColor; flashRoutine = null; } private IEnumerator Flash3DRoutine(Renderer rend) { var mat = rend.material; // instance of material Color originalColor = mat.color; float elapsed = 0f; while (elapsed < flashDuration) { mat.color = flashColor; yield return new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); elapsed += flashInterval; mat.color = originalColor; yield return new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); elapsed += flashInterval; } mat.color = originalColor; flashRoutine = null; } private void PlaySound(AudioClip clip) { if (audioSource != null && clip != null) { audioSource.Stop(); // stop any current sound audioSource.clip = clip; audioSource.Play(); // play new sound } } private void SendHaptics() { if (hapticPlayer == null) return; if (hapticFrequency > 0f) // with frequency (OpenXR) hapticPlayer.SendHapticImpulse( hapticAmplitude, hapticDuration, hapticFrequency ); else // simple impulse hapticPlayer.SendHapticImpulse( hapticAmplitude, hapticDuration ); } } - Add a
- Configure the Script:
Audio Source: Assign anAudioSourcecomponent. Leave the “Audio Clip” field in the AudioSource blank. The script will dynamically assign the appropriate clip at runtime.Motor Hum Clip: Assign a sound to play when the robot starts moving (e.g., mechanical hum or activation tone).Idle Beep Clip: Assign a sound to play when the robot returns to idle (e.g., soft beep or chime).Flash Duration: Set how long the button should flash overall (e.g.,3seconds).Flash Color: Choose the color that the button should blink (typically yellow for feedback).Flash Interval: Set how fast the button should blink (e.g.,0.2seconds per on/off cycle).XR Controller: Drag in theLeftHand ControllerorRightHand ControllerGameObject from yourXR Rig.
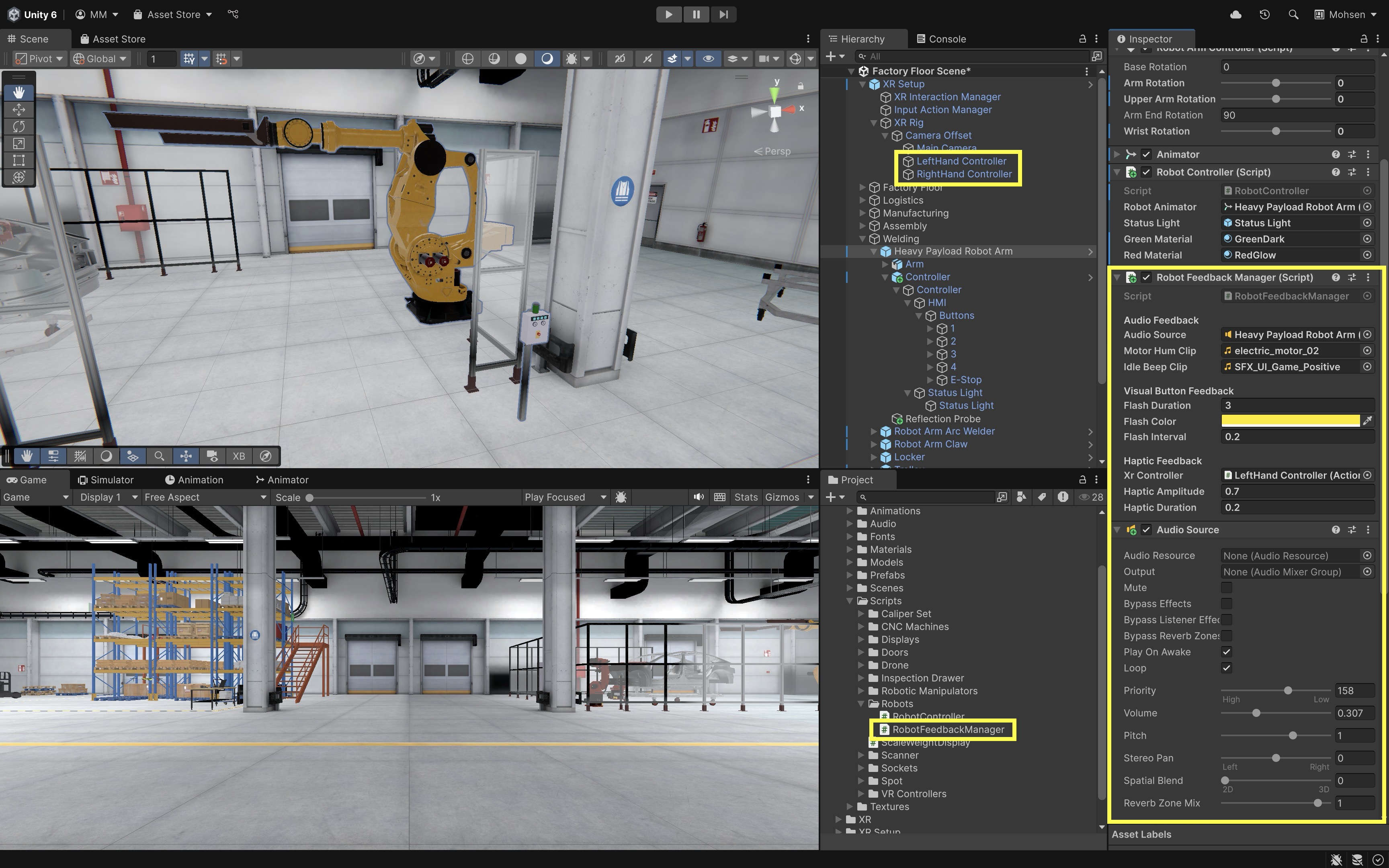
- Trigger Feedback on Button Event:
- In the
Button (Script)component, go to theOnClick()event list. - Click the
+button to add a second event. - Drag the robot GameObject (
Heavy Payload Robot Arm) into the event slot. - From the dropdown, select
RobotFeedbackManager → OnRobotStartMoving()(this enables auditory feedback). - Click
+again to add a third event. - Drag the robot GameObject into this slot.
- From the dropdown, choose
RobotFeedbackManager → FlashButton(GameObject)(this enables visual feedback). - Drag the
same button GameObjectinto the argument field. - Repeat the above for all numpad buttons.
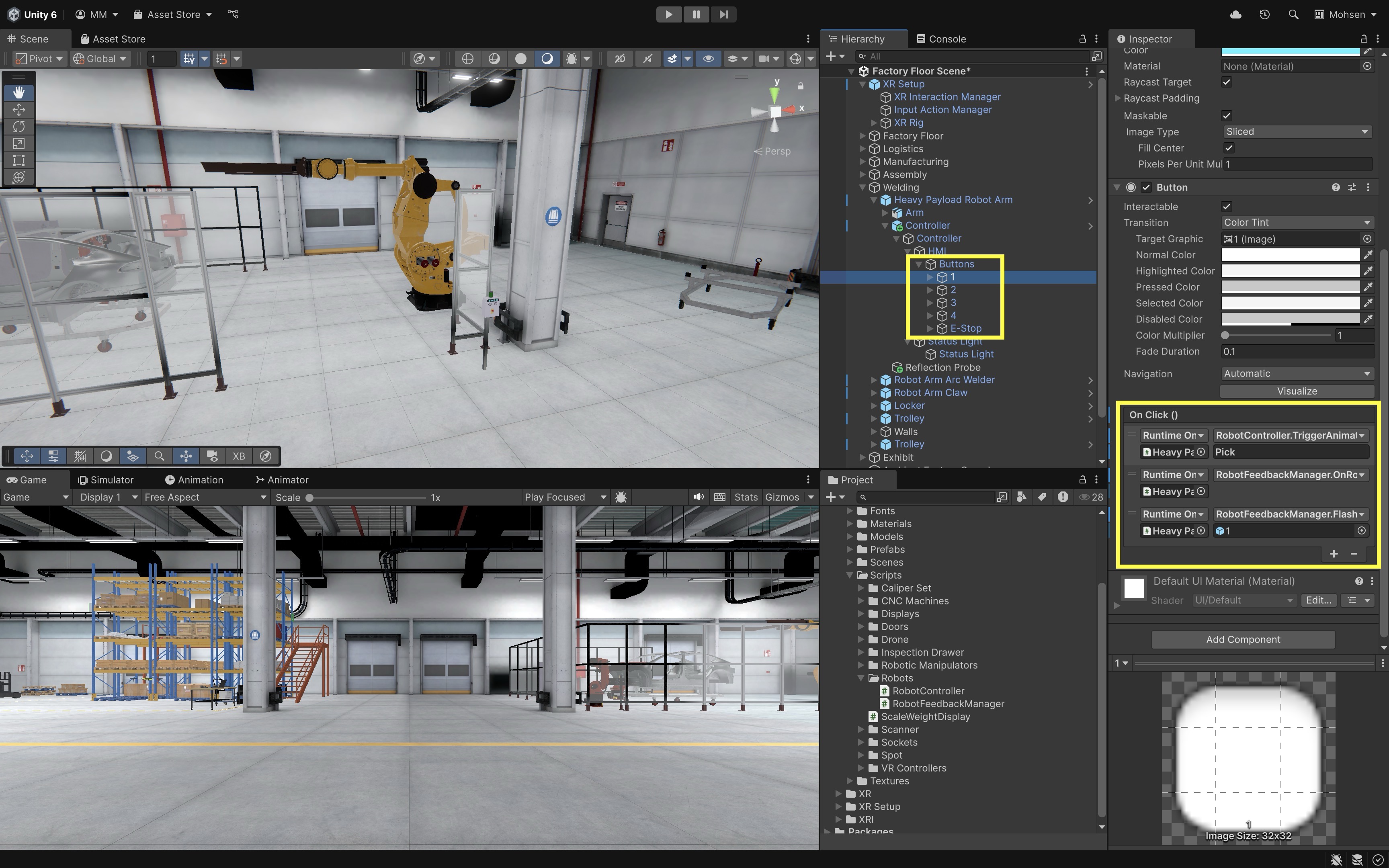
- In the
- Trigger Feedback on Animation Event:
- In the
Animator, go to the end of yourRobot Arm Idleanimation. - Add an
Animation Eventto the last frame. - Set the function to
OnRobotReturnToIdle.
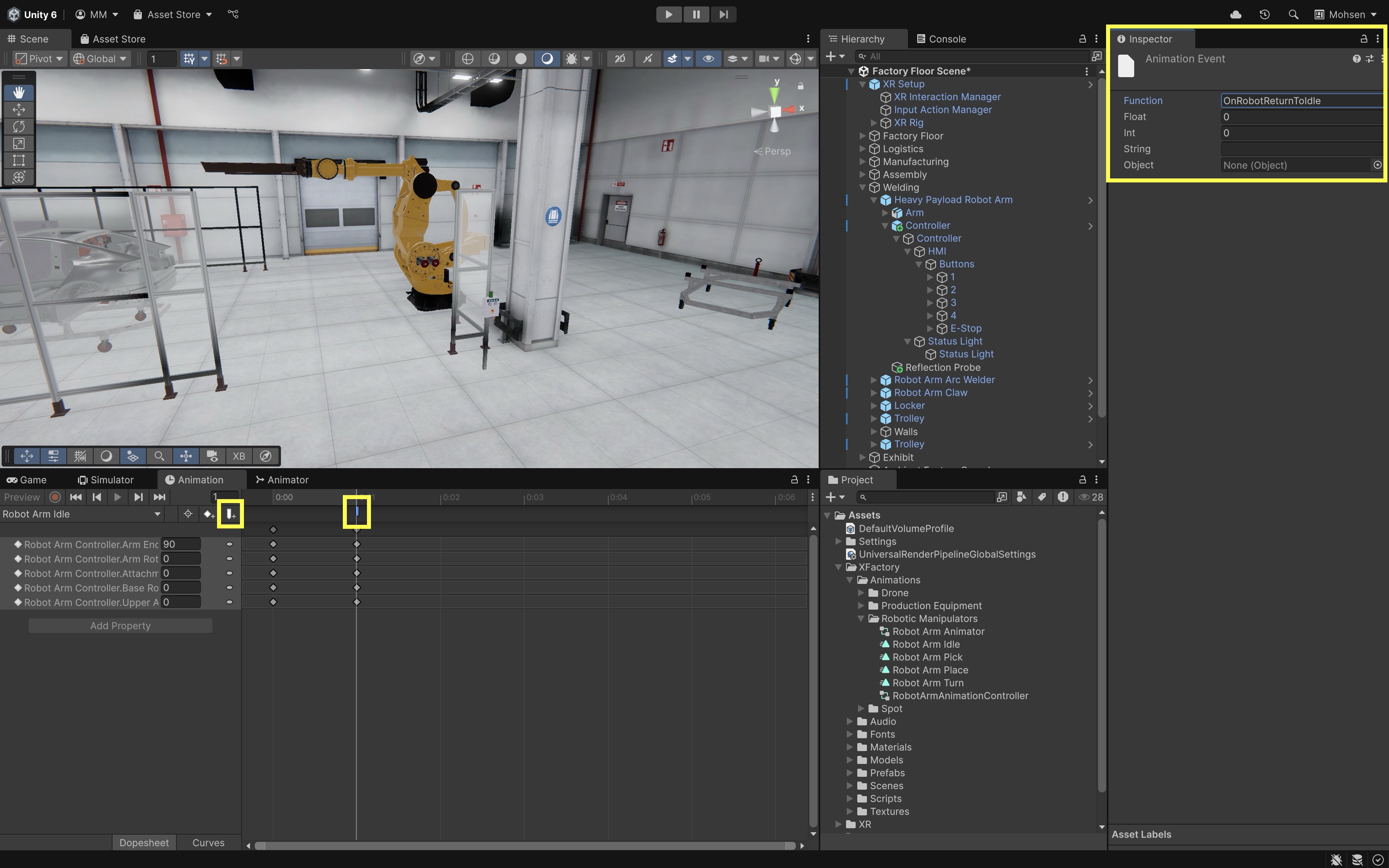
- In the
- Deploy and Test:
- When the robot is activated (e.g., via numpad button), the status light turns red, a motor hum sound plays, and the user’s controller vibrates (haptic pulse).
- When the robot returns to idle (triggered by animation event at the end of the idle animation), the status light turns green, and a beep (or idle motor) sound plays
This feedback loop simulates a real-world factory machine’s behavioral cues, enhancing immersion, safety, and real-time situational awareness for learners.
Contextual Interactions
Contextual interactions are dynamic behaviors in which the available actions, controls, or responses adapt to the current state or condition of the virtual system. In engineering and industrial XR scenarios, these interactions enforce safety protocols, guide users through proper sequences, and ensure that every operation reflects real-world constraints. Such contextual interactions reinforce real-world discipline—only allowing users to tighten a virtual valve once the pressure gauge reads safe levels, or preventing tool activation until protective shielding is verified—so that virtual practice mirrors the careful sequence of industrial procedures.

Core Concepts
-
System State Awareness: The XR environment continuously monitors key parameters—such as machine power status, emergency-stop flags, or calibration levels—and enables interactions only when conditions are valid. For example, a virtual CNC lathe will lock out its control panel until the spindle is fully stationary and safety guards are in place.
-
State-Dependent Behavior: User inputs can be transformed or blocked depending on operational modes. In “maintenance” mode, a virtual robot arm might allow direct joint manipulation, whereas in “production” mode the same gestures instead trigger pre-programmed routines. This ensures users cannot accidentally invoke inappropriate actions for the current context.
-
Safety by Design: Contextual rules simulate industrial interlocks, lockouts, and emergency-stop procedures. Attempting to open a virtual control cabinet without first disabling power might trigger an automatic shutdown or require a confirmation sequence—teaching users the importance of procedural compliance and preventing hazardous mistakes.
-
Feedback on Invalid Interactions: Whenever an action is blocked or modified, the system provides clear, contextual cues: a red overlay on a disabled button, a “lock” icon appearing on a tool handle, an audible warning tone, or a brief on-screen message explaining why the operation is unavailable. This immediate, informative feedback helps users correct their workflow without confusion.
Custom Unity Events
At the welding station of XFactory, an emergency stop button governs the entire robot operation. If the e-stop is engaged, the numpad is disabled, any button press triggers a buzz alarm and a flashing red status light, and robot animations are blocked to simulate faulty state. If the e-stop is cleared, however, normal operation resumes, the light returns to solid green, sounds are reset and input is re-enabled. Here is how to implement this behavior:
- Create a System Manager Script:
- Create a new empty GameObject (
System Manager) as a child ofHeavy Payload Robot Arm. - Attach the following script to
System Managerto manage the global system state and toggles interaction accordingly.
using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.Events; public class SystemStateManager : MonoBehaviour { public bool isEmergencyStopped = false; public UnityEvent onEStopEngaged; public UnityEvent onEStopCleared; public void ToggleEmergencyStop() { isEmergencyStopped = !isEmergencyStopped; if (isEmergencyStopped) { Debug.Log("Emergency Stop Engaged"); onEStopEngaged?.Invoke(); } else { Debug.Log("Emergency Stop Cleared"); onEStopCleared?.Invoke(); } } } - Create a new empty GameObject (
- Configure the Script in the
Inspector:- Leave
isEmergencyStoppedunchecked (default is normal state). - Under
onEStopEngaged(when e-stop is pressed), click the+button. Add each numpad button individually. AssignButton → bool interactableand uncheck the box to disable interaction during emergency stop. - Under
onEStopCleared(when e-stop is reset), click the+button again. Add the same objects. AssignButton → bool interactableand check the box to re-enable interaction when normal operation resumes.
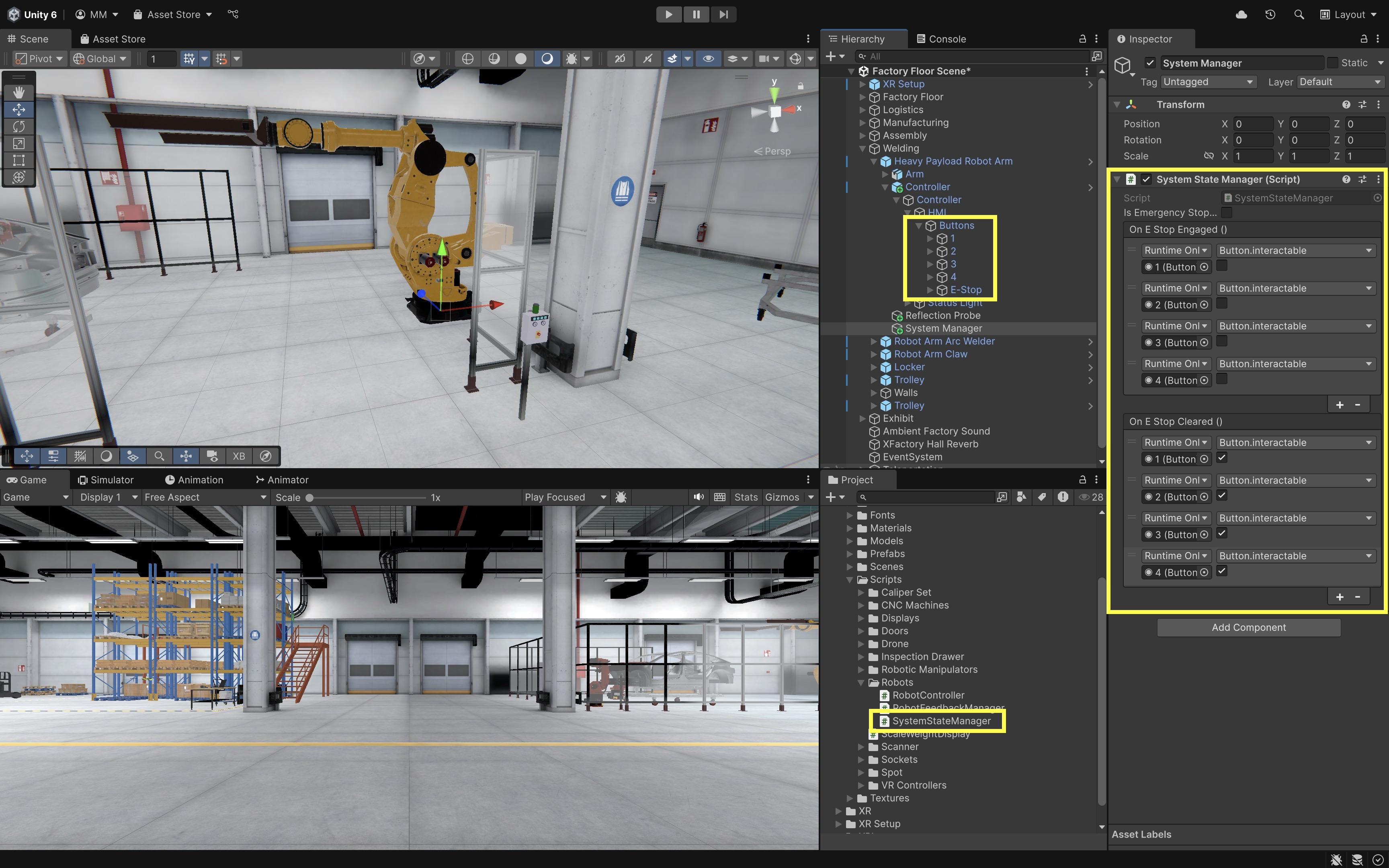
- Leave
- Update
RobotController.csto Check State:- Modify your
RobotController.csto respect the emergency stop:
using UnityEngine; public class RobotController : MonoBehaviour { public Animator robotAnimator; public GameObject statusLight; public Material greenMaterial; public Material redMaterial; public SystemStateManager systemStateManager; public RobotFeedbackManager feedbackManager; private Renderer statusRenderer; // Name of the idle state as it appears in the Animator private const string idleStateName = "Robot Arm Idle"; private void Start() { if (statusLight != null) statusRenderer = statusLight.GetComponent<Renderer>(); } private void Update() { if (robotAnimator == null || statusRenderer == null) return; bool isInTransition = robotAnimator.IsInTransition(0); AnimatorStateInfo currentState = robotAnimator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0); // Light should only be green if not in transition and fully in the idle state bool isTrulyIdle = !isInTransition && currentState.IsName(idleStateName); statusRenderer.material = isTrulyIdle ? greenMaterial : redMaterial; } public void TriggerAnimation(string triggerName) { if (systemStateManager != null && systemStateManager.isEmergencyStopped) { Debug.Log("Blocked: System is in Emergency Stop"); feedbackManager?.OnEmergencyBlocked(); return; } if (robotAnimator == null) return; robotAnimator.SetTrigger(triggerName); feedbackManager?.OnRobotStartMoving(); Debug.Log($"Robot Triggered: {triggerName}"); } } - Modify your
- Configure the Script:
- Select the robot GameObject with
RobotController.cs. - In the
System State Managerfield, drag in theSystem ManagerGameObject (the one with theSystemStateManager.csscript). - In the
Feedback Managerfield, assign the robot itself (which contains theRobotFeedbackManager.csscript).
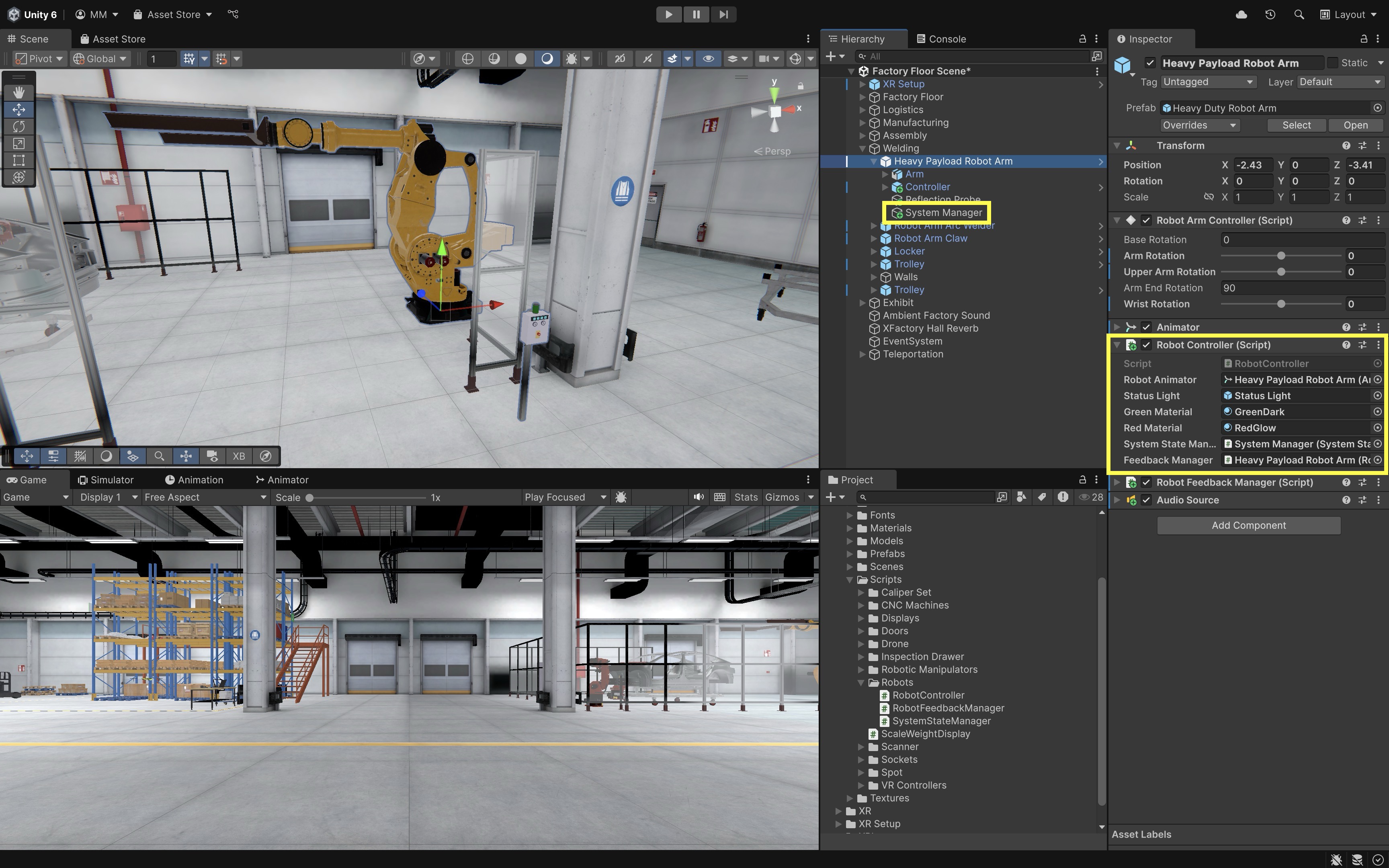
- Select the robot GameObject with
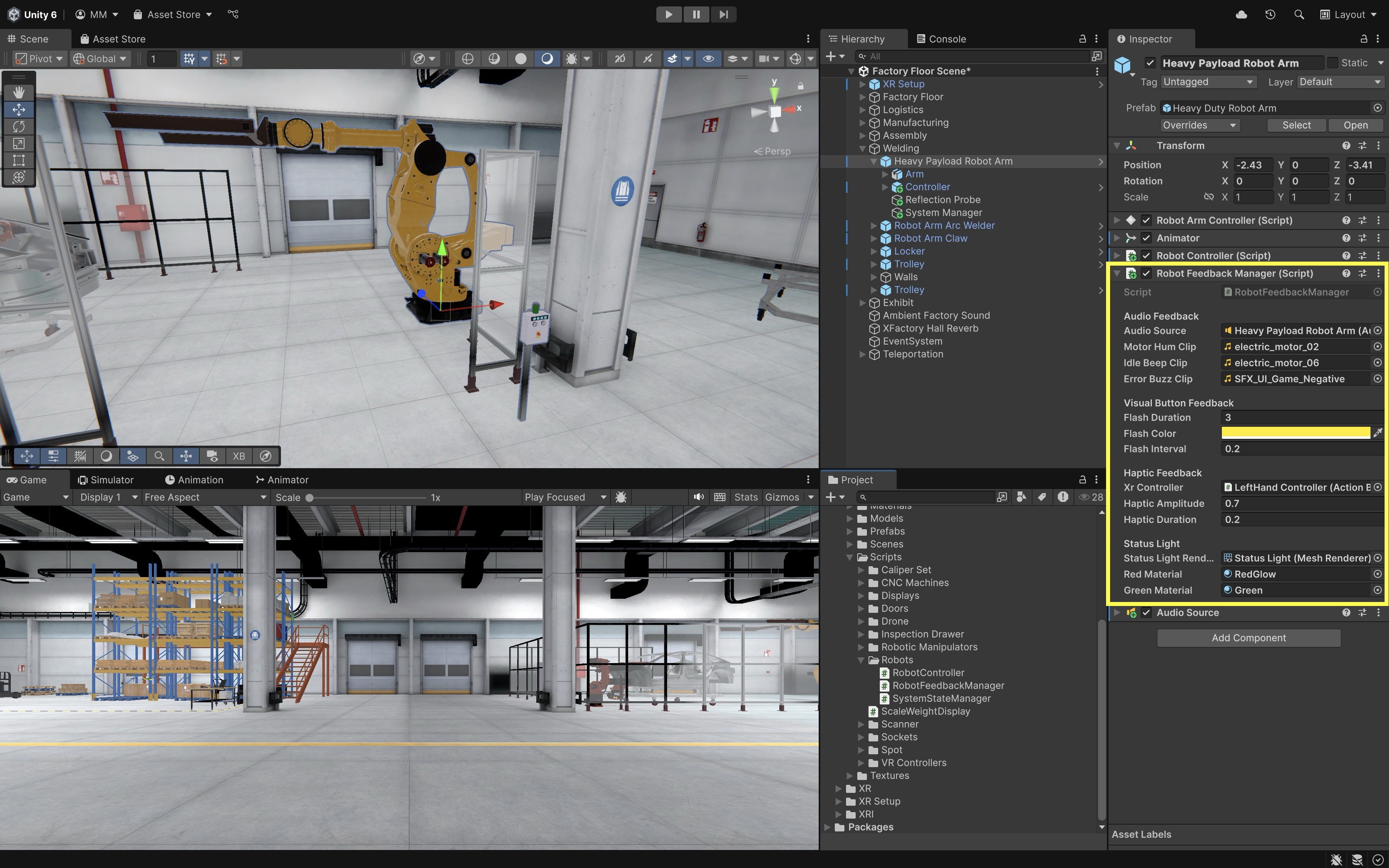
- Add Emergency Feedback to
RobotFeedbackManager.cs:- Expand the
RobotFeedbackManager.csto support flashing and buzzing.
using UnityEngine; using UnityEngine.UI; using System.Collections; using UnityEngine.XR.Interaction.Toolkit.Inputs.Haptics; public class RobotFeedbackManager : MonoBehaviour { [Header("Audio Feedback")] public AudioSource audioSource; public AudioClip motorHumClip; public AudioClip idleBeepClip; [Header("Visual Button Feedback")] public float flashDuration = 0.5f; public Color flashColor = Color.yellow; public float flashInterval = 0.1f; [Header("Haptic Feedback (XRI 3.x)")] [Tooltip("HapticImpulsePlayer on the hand/controller object (Left or Right).")] public HapticImpulsePlayer hapticPlayer; [Range(0f, 1f)] public float hapticAmplitude = 0.7f; public float hapticDuration = 0.2f; [Tooltip("Optional (requires proper binding to a Haptic control).")] public float hapticFrequency = 0f; [Header("Status Light")] [SerializeField] private Renderer statusLightRenderer; [SerializeField] private Material redMaterial; [SerializeField] private Material greenMaterial; [SerializeField, Tooltip("Blink cadence for the emergency status light.")] private float statusFlashInterval = 0.5f; [Header("Emergency Feedback")] public AudioClip errorBuzzClip; // Coroutines private Coroutine flashRoutine; // UI/mesh button flash private Coroutine statusFlashRoutine; // emergency status light flash // --- Public API ---------------------------------------------------------- public void OnRobotStartMoving() { PlaySound(motorHumClip); SendHaptics(); } public void OnRobotReturnToIdle() { PlaySound(idleBeepClip); } public void OnEmergencyBlocked() { StartFlashingRed(); PlaySound(errorBuzzClip); } public void OnEmergencyCleared() { StopFlashing(); SetLightMaterial(greenMaterial); if (audioSource != null) audioSource.Stop(); } public void FlashButton(GameObject button) { if (button == null) return; var img = button.GetComponent<Image>(); if (img != null) { if (flashRoutine != null) StopCoroutine(flashRoutine); flashRoutine = StartCoroutine(FlashUIRoutine(img)); return; } var rend = button.GetComponent<Renderer>(); if (rend != null) { if (flashRoutine != null) StopCoroutine(flashRoutine); flashRoutine = StartCoroutine(Flash3DRoutine(rend)); } } // --- Coroutines: Button Flash ------------------------------------------- private IEnumerator FlashUIRoutine(Image img) { Color originalColor = img.color; float elapsed = 0f; var wait = new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); while (elapsed < flashDuration) { img.color = flashColor; yield return wait; elapsed += flashInterval; img.color = originalColor; yield return wait; elapsed += flashInterval; } img.color = originalColor; flashRoutine = null; } private IEnumerator Flash3DRoutine(Renderer rend) { var mat = rend.material; // instance Color originalColor = mat.color; float elapsed = 0f; var wait = new WaitForSeconds(flashInterval); while (elapsed < flashDuration) { mat.color = flashColor; yield return wait; elapsed += flashInterval; mat.color = originalColor; yield return wait; elapsed += flashInterval; } mat.color = originalColor; flashRoutine = null; } // --- Coroutines: Emergency Status Light --------------------------------- private void StartFlashingRed() { if (statusFlashRoutine != null) return; statusFlashRoutine = StartCoroutine(FlashRed()); } private void StopFlashing() { if (statusFlashRoutine != null) { StopCoroutine(statusFlashRoutine); statusFlashRoutine = null; } } private IEnumerator FlashRed() { if (statusLightRenderer == null || redMaterial == null || greenMaterial == null) yield break; var wait = new WaitForSeconds(statusFlashInterval); while (true) { statusLightRenderer.material = redMaterial; yield return wait; statusLightRenderer.material = greenMaterial; yield return wait; } } // --- Helpers ------------------------------------------------------------- private void PlaySound(AudioClip clip) { if (audioSource != null && clip != null) { audioSource.Stop(); audioSource.clip = clip; audioSource.Play(); } } private void SendHaptics() { if (hapticPlayer == null) return; if (hapticFrequency > 0f) hapticPlayer.SendHapticImpulse(hapticAmplitude, hapticDuration, hapticFrequency); else hapticPlayer.SendHapticImpulse(hapticAmplitude, hapticDuration); } private void SetLightMaterial(Material mat) { if (statusLightRenderer == null || mat == null) return; statusLightRenderer.material = mat; } private void OnDisable() { // Ensure coroutines are stopped if object is disabled/destroyed if (flashRoutine != null) { StopCoroutine(flashRoutine); flashRoutine = null; } StopFlashing(); } } - Expand the
- Configure the Script:
Error Buzz Clip: Assign a short alert/buzzer audio clip.Status Light Renderer: Drag in theRenderercomponent of the robot’s status light (Status Light).Red Material: Assign a red material used to indicate emergency.Green Material: Assign a green material used to indicate normal operation.
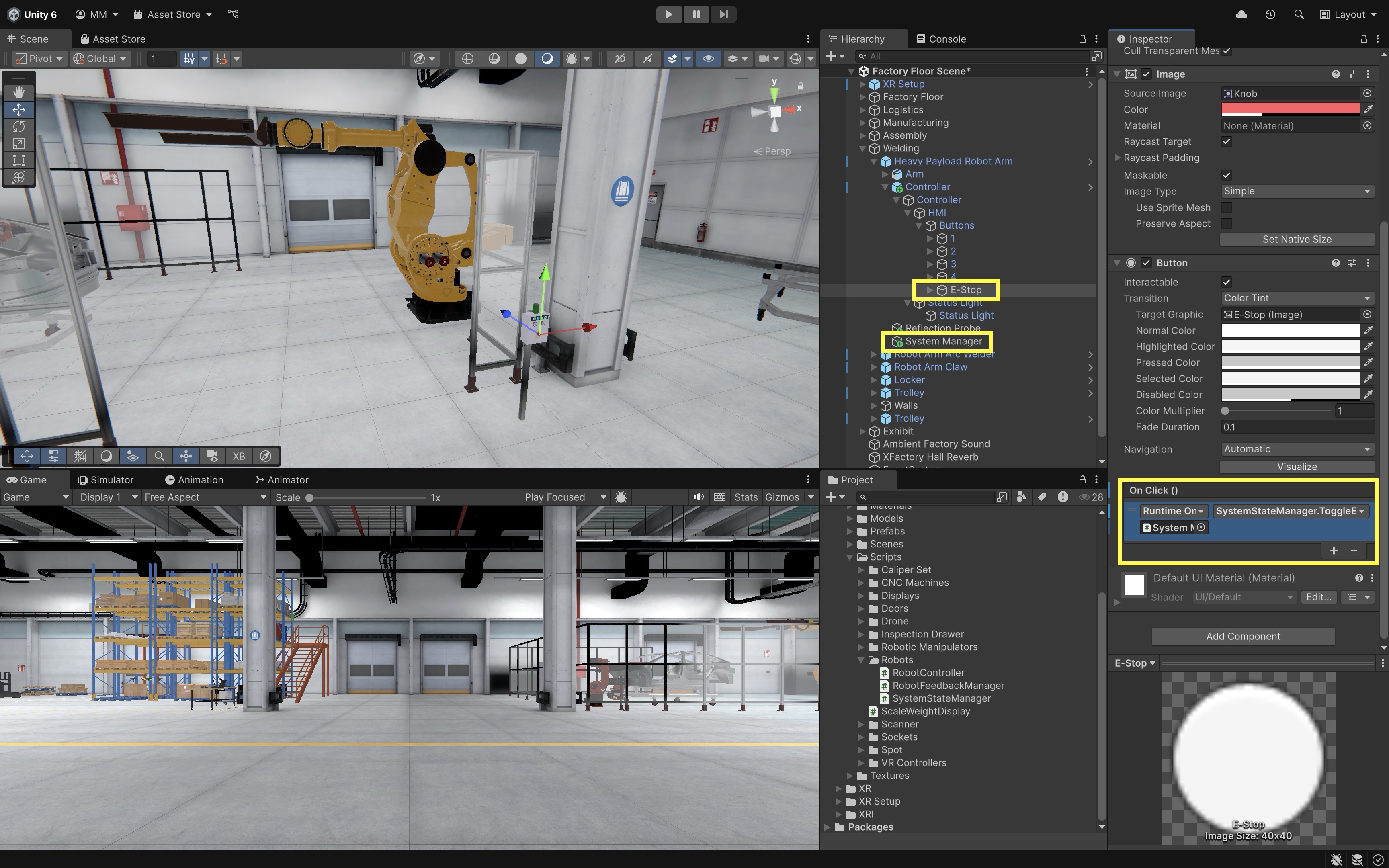
- Hook Up the Emergency Stop Button:
- In the
E-Stopbutton’sInspector, locate theOnClick()event section. - Click the
+to add a new event. - Drag the
System ManagerGameObject (the one withSystemStateManager.cs) into the object field. - From the dropdown, select
SystemStateManager → ToggleEmergencyStop(). This enables toggling the emergency state on and off when the e-stop is pressed.
- In the
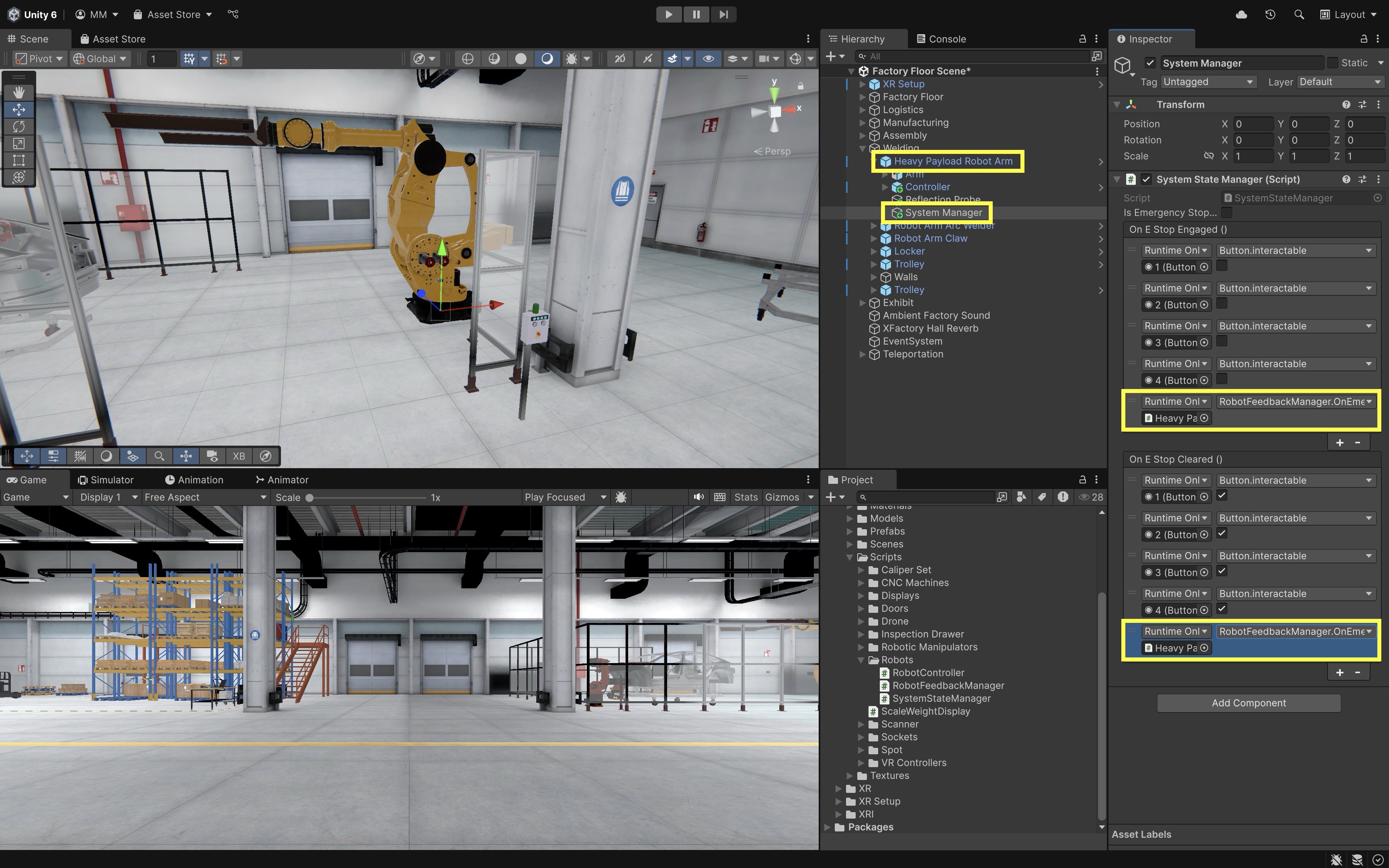
- Wire Unity Events in the
Inspector:- Use Unity Events to link state transitions to visual and audio feedback.
- Locate the
SystemStateManagercomponentOn E-Stop Engaged. DragHeavy Payload Robot Arminto the field and callRobotFeedbackManager.OnEmergencyBlocked(). - Similarly, locate
On E Stop Clearedand callRobotFeedbackManager.OnEmergencyCleared()
- Deploy and Test:
- Robot control is disabled during an emergency stop.
- Pressing any number on the numpad while the e-stop is active results in a flashing red status light, a buzz alarm sound, and no animation is triggered on the robot.
- Releasing the e-stop (pressing again) returns the system to normal. The status light turns solid green, the buzzing stops, the numpad becomes interactive again, and robot controls are re-enabled.
This reflects real-world industrial safety behavior, where all interactive systems respect current operational context, promoting safety, realism, and reliable user feedback.
Key Takeaways
Activating objects in VR within Unity’s XR framework hinges on an event-driven approach that connects user inputs to specific actions through well-structured events, listeners, and handlers. By decoupling interaction logic from the actions performed, developers can create modular, maintainable systems that are easy to extend or reconfigure. Effective implementation blends multi-modal feedback—visual, auditory, and haptic cues—to reinforce system responses and keep users informed, while contextual interaction logic ensures operations respect current states and safety conditions, such as disabling controls during an emergency stop. Together, these principles not only enhance immersion and usability but also model real-world engineering practices and safety protocols.